CFHT/OASIS를
이용한 Seyfert 은하핵 연구
1. Scientific background
What kind of observation or measurements?
To disentangle contributions of nuclear
and shock induced photoionization;
To quantify the energy budget of NLR
gas from fast shocks and comparison with P-I
|
Most AGN studies - emission line gas in [E]NLR
- How [E]NLR is related to ionizing nuclear
radiation and ejecta
Two dominant ionizing source in NLR gas
- Central engine itself
- Extreme ultraviolet radiation by hot (shocked)
gas
Main difficulty is distance (spatial resolution of shock structures)
|
|
1.1 Motivation
Active Galaxies (low density jet material, nonthermal radio
emission, strong external source of ionizing radiation)
Cf. Herbig-Haro objects (jet material denser than
the ambient medium)
Difficult job - situations, connection?
1.2 examples of spatially shock structures in a
few nearby Seyfert galaxies.
|
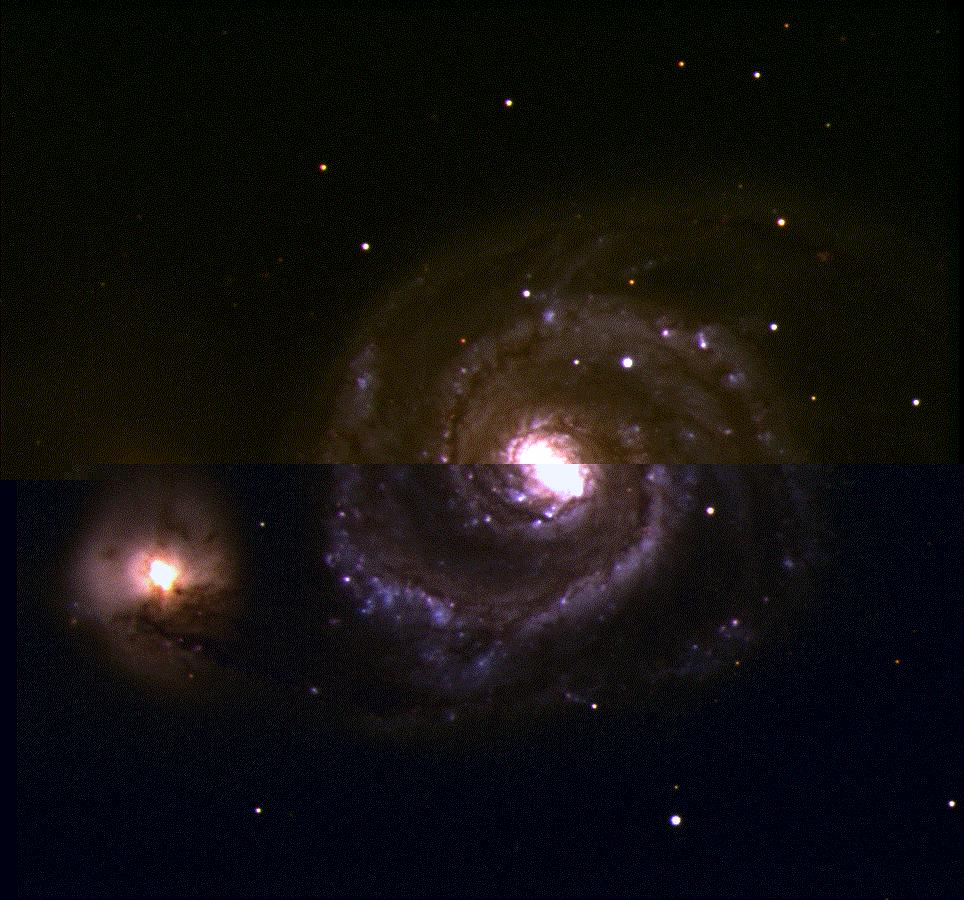
M51, NGC 5194 (Seyfert 은하)
Last 15 years,
M51: Cecil 1998,
NGC 1068 : Wilson & Ulvestad 1987
Circinus : Veilleux & Bland-Hawthorn 1996
NGC 4258 : Cecil et el. 2000
|
|
|

|
2. Goal & scientific objectives
We propose to observe some of spatially resolved bubbles
and bow shocks with the 3D spectrograph OASIS
프랑스 Lyon 천문대의 Dr. Ferruit 와 천문연구원
형식 박사가 CFHT/OASIS를 이용하여, Seyfert은하를
2001년 3월 13-18일 공동으로
관측
Test the predictions of bow shock models using bow
shocks in NGC 4258 and NGC 1068
Test the relationship between optical emission and
the input of mechanical energy in presence of nuclear radiation
- southern bubble structure (XNC)
in M 51
|

M51, NGC 5194 (Seyfert G.)
|
|
|

NGC 4258 (Sey-2 G)
|
3. OASIS(Optically Adaptive System for Imaging Spectroscopy)
3.1 Brief history
- TIGER 1 prototype 이 만들어진 후 다음과 같은
개선이 있었다(G.Court, Obs. de Lyon & Marseille).
80 spectra, 1.2 arcsec in 1987
0.7 arcsec in
1990s
Adaptive optics ------------> New
IFS
- OASIS at CFHT
First Engineering (F/20 adaptive & F/8)
Many observing run scheduled for March 1998
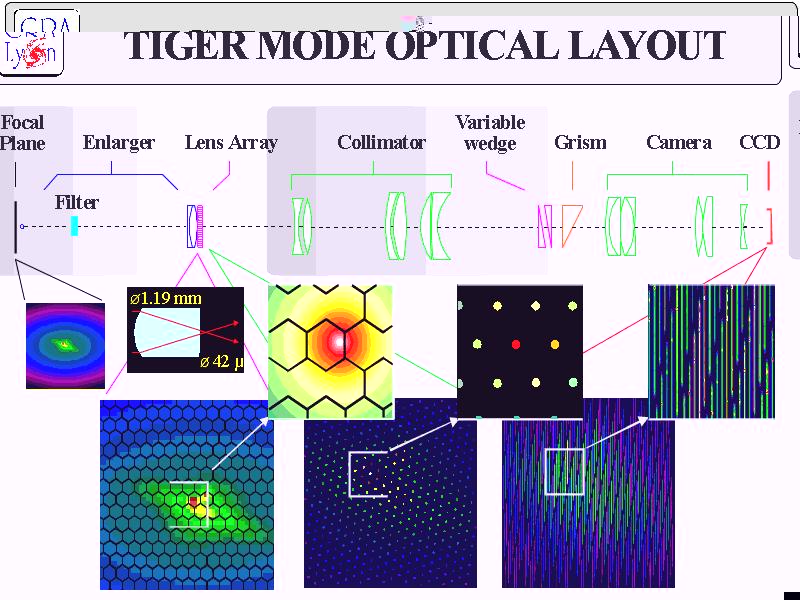
3.2 TIGER mode optical layout:
3.3 TIGER MODE (spectroscopy):
O. 1200 spectra of 400 resolved
spectral elements
O. Spectral resolution =
Sky sampling (Field)
1)
F/20 AOB
0.04"
(1.6 " × 1.2 "), 0.11 " (4.1 " × 3.3 "),
0.16 "(6.2 " × 5.0 "), 0.30 "
(11" × 9 ")
2)
F/8 Cassegrain
0.27
" (10.4 " × 8.3 "), 0.41 " (15 " ×
12 ")
O. Spectral resolution configuration
(2A or 1A per pixel)
MR1
(4760 - 5558A), MR2 (6210 - 7008A), HR4 (6492 - 6838A), MR0, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, HR1, 2, 3, 5
[O III]
5007A, [N II] 6584/48A, H?, H?
4. Seyfert observations
2001년 3월에 관측된 Seyfert 은하는 Mrk 34, NGC 2992, NGC
4051, NGC 4253, NGC 4258, NGC 5728, M51이다.
사용된 기기의 setting은 MR2 (6210-7008A), MR1 (4760-5558A),
0.41"/0.27" 로 노출시간은 2 × 30min, 45min 등이었다.
Mrk 34 - MR1 MR2 F/8 0.41", NGC 4253 - MR2 F/8 0.27"
, NGC 4258 - HR4, MR2 F/8 0.41", NGC 5548 - MR1, MR2 F/8 0.27"
NGC 4051 - MR2 F/8 0.41", NGC 5728 - MR1 MR2
F/8 0.41"
4.1 Seyfert 2 galaxy
|
Mrk 34 (2), a double radio source with separation
2.4” (2.2kpc)
|
|
High resolution VLA observation:
time variable (5" north)이 존재하는 은하이다.
|
|
|

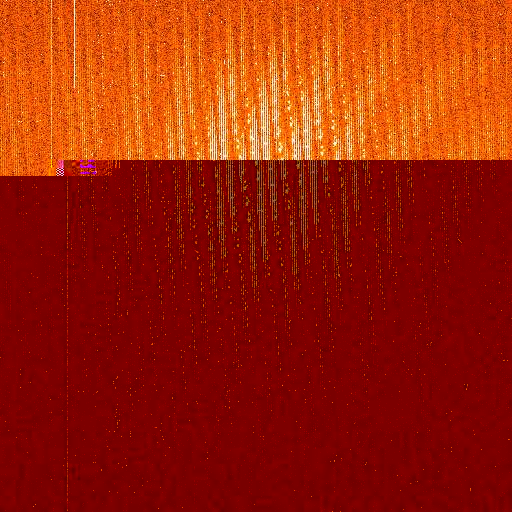
|
4.2 Seyfert 2 glaxy (dusty)
|
Sa galaxy, almost edge-on으로
NGC 2992 (2), 0.00771 (223.59), Dust
C, strongly interacting!
X-ray emission on a 2 kpc size scale
(Narrow-line X-ray galaxy)
Narrow-line with possible weak-broad
line (optical)
|
|

|
|
|
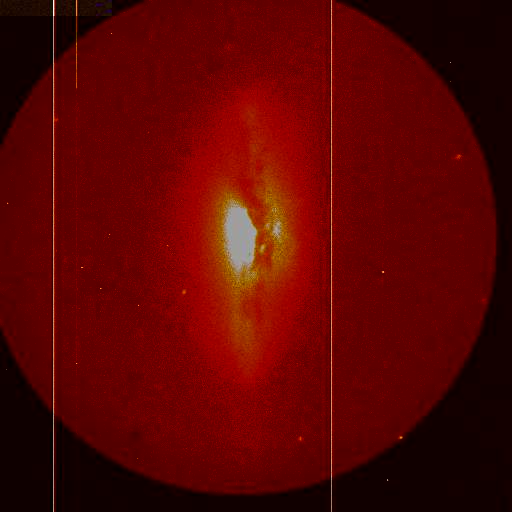
|
|

|
4.3 Seyfert 1 galaxy
1.Sprial arms emanate from a bar?
2.Nucleus: least luminous classical type I Seyfert
|
NGC 4051 (1) radio jet PA =18o, Many HII regions along
S-arms
|
|

Host galaxy SABbc, circumnulcear emission ~ 8"
|

Narrow-line Seyfert 1 nuclei (Osterbrock &
Pogge 1985)
|
|

Trigered by interaction with NGC 4013?
|
5. Analysis - Active jet and associated shocks
NGC 4258 HST/WFPC2 image
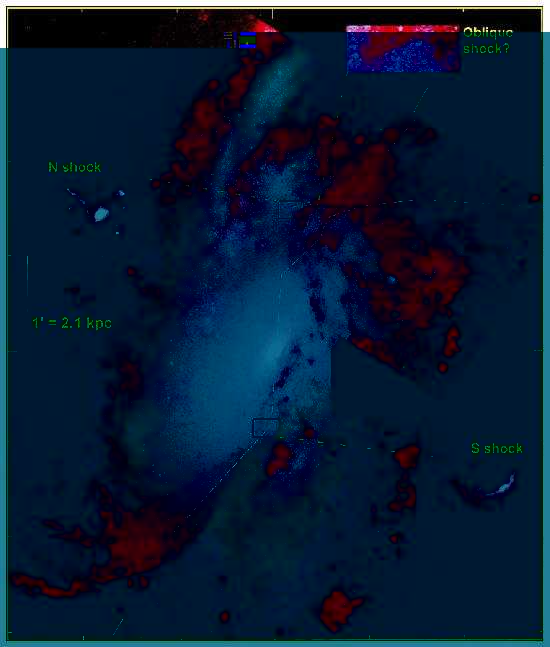
Cecil et al. (2000 ApJ) - Halpha+[NII] 6400sec 0.455"
|
Reduced Image(s) 완성된 이미지의 모습
|
NGC 4258 (bowshock)
Reduction with XOasis
3 × 45min + 1hr (lens 487)
|
분광선 lens 487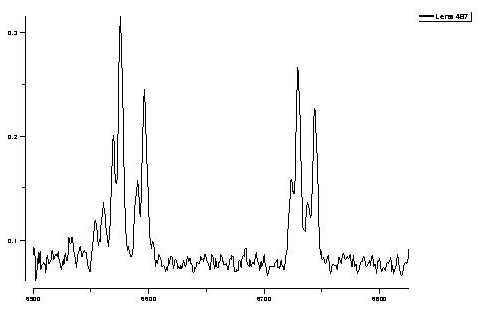
Kinematics which is not available with HST WFPC2
(cf. STIS long slit)
|
Theoretical analysis: Shock in jet (PN, AGN)
Photoionization & Shock heating (intensities
& profiles)?
|
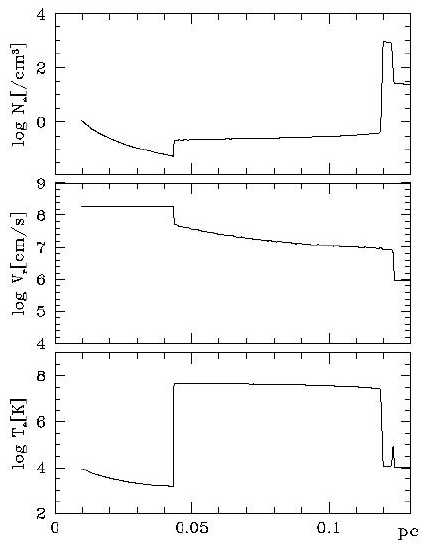
|
밀도 (density diagnostics)
[S II], [O II] lines
속도 (Kinematics)
line profiles
온도를 알 수 있는 분광선
[OIII] 4363/5007A
Inner P-I
outer - shocks (t_hyd << t_cool)
|
6. plan, current job, etc..
HST관측에서 제시하지 못한 운동 역학적 (kinematics) 정보를 얻게 됨
Adopt a 2-dimensional gas-dynamic code method and predict the lines, we need
(trade-off)
We cannot adopt the high resolution of hydrodynamics.
Thus, we must take a slice, shell fragmentation
a jet (80도 - 90도) )polar zone
Application to Jet, AGN NLR cone, torus BLR, accretion disk
참고 사항 : OASIS는 2002년 하반기에 WHT으로 옮길예정임
|
2002B to WHT (U.K.) 협상 중
첫해 7-10일
다음해부터 4일 이용시 하루
|
|